|
Q: "No Dial Tone" error?
If you receive a NO DIAL TONE result code or cannot get the modem to dial:
You will need to see if there is any software accessing the modem, such
as a FAX program, that may be running in the background. If you are new to the
Internet and (or) computers, you may have a program waiting for a call -
accessing the modem - and not even know it. The easiest way to check to see
what programs are running, in Win95 & Win98, is to press CTRL+ALT+DEL keys, in
succession, on the keyboard. This will bring up the "Close Program" dialog
box. Highlight the program that is accessing the modem and click on the
"End Task" button. This will close that particular program. If you still get
the NO DIAL TONE error, go back and try closing other programs until you
close the correct one.
If you do find which program was accessing your modem, the cuplrit could be in
your "Start-up" folder and loading when Windows first boots up. Go to your
start-up folder, in the Windows directory on your "C" drive, and remove the
short cut to that program.
If you sill are not able to dial out or get "NO DIAL TONE"
error, one of the following may be the problem.
- The Phone line you are using may not be working. Verify this with a
telephone connected on the same line as the modem. Listen for a dial tone.
- Make sure you have the correct cable to go between the F jack and your
modem. We recommend the SMC 911 cable.
- Ensure that the modem is correctly installed via the Control Panels | Modems |
Diagnostics | More Info.
- You have too many devices on the line. Try unplugging all other phone
devices connected to your phone line: FAX machines, answering machines,
line filters, etc.
- Your phone line may be plugged into the wrong jack. On your modem,
make sure your phone line is plugged into the (telco)LINE jack and your
telephone is plugged into the PHONE jack.
- If you must first dial a zero (0) to get an outside line,
ensure that is selected in you connection dialing preferences. If you have to dial a nine (9)
to get an outside line, add 2 commas after the 9 and before the number. (example: 9,,8127000)
This will give a slight pause, to regain dial tone, before the modem dials Internet Junction.
- If you use a PABX (TK-Anlage) in your home or office and you use an analog modem,
uncheck "wait for dial tone" in the modem properties in Windows 95 and NT.
- Your modem may be damaged. The Tampa Bay area is in the TOP 10 in the
number of lightning strikes per year. It doesn't take much voltage to render
a modem inoperable. Do what the IJ technicians do...
ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE MODEM LINE DURING A THUNDERSTORM. If your modem
is damaged, please contact your modem manufacturer.
- If you have the GTE Personal Secretary and you have messages waiting,
you may receive a NO DIAL TONE ERROR.

Q: "Cannot Establish a Dialup Network Connection" error?
If you receive a Cannot Establish Dial-up Network Connection error:
- Check your username and password. Both of them are case sensitive and must be entered
exactly as we have them on our computer to access the network.
- Ensure that TCP/IP is loaded and selected in your dialup networkingl settings.
- Both of the above are correct but you still cannot logon - same error. Please call our technical
support hot line at 813-855-7793. There may be an account problem or simply a password discrepency.

Q: Modem cannot be found (detected automatically) under Windows 95?
Use the following steps, by process of elimination, to solve the
problem.
- Check the jumper setting, make sure the COM Port and IRQ settings
are correct.
- For internal modems: check the modem card itself, is it seated in
the slot properly?
After you have installed your modem, Windows 95 should:
- Recognize your modem
- Assign a unique COM port and IRQ for your modem to use
(if modem is Plug and Play)
Use the following steps, by process of elimination, to solve the
problem.
1. In Windows 95, select Start | Settings | Control Panel | Modems | Diagnostics.
Highlight the COM Port your modem is on and then click on More Info.
- If Windows 95 can communicate with the modem, then the modem driver
is functioning correctly (If you get a window with ATI commands and an
OK button at the bottom, you're in business). If you don't get this
screen, highlight a different COM Port and try More Info once again.
- If Windows 95 shows an error message in the More Info box
(something like " Couldn't Open Port"), go to step 2.
2. In Windows 95, select Start | Settings | Control Panel, click on
the System icon and then Device Manager.
3. In Device Manager, if you see any yellow circle icons, remove
them all by highlighting, clicking on Remove, until all of the
yellow ones are gone.
4. Click on Modems in Device manager. Remove all modems listed by
selecting one, clicking on Remove, until they all gone.
5. Click on Ports in Device Manager. Remove all ports.
6. In Device Manager, if you have an item called Unknown Devices or
Other Devices, remove all entries in this section by selecting
one, clicking on Remove, until they all gone.
7. Verify that you have no Modem, Port, or "Unknown Devices or
Other Device" entries in the Device Manager.
8. Select Start, then Shutdown, and turn off your computer (with
the POWER button - COLD BOOT.
9. Let the computer sit for at least 60 seconds. Turn on your
computer. If the New Hardware Found dialog box appears, you
need to install a modem driver file. If the New Hardware Found
box does not appear, Windows 95 already has a driver for
your modem.
10. Click "Driver from disk provided by hardware
manufacturer."
11. Click OK.
12. Insert the Modem Utility Disk that came with your modem in
drive A: (use the appropriate driver letter if the floppy
drive is not drive A). If your software is on CD-ROM, use the
appropriate driver letter for your CD-ROM drive (usually D: or E:)
13. Click OK. Select Start | Settings | Control Panel |
Modems | Diagnostics, and then More Info. If Windows 95 does
NOT return an error message, the modem driver is functioning
correctly. That is all this means. (It does NOT necessarily mean
that your modem will connect to the Internet)
14. Eject the disk or CD-ROM and store it in a safe place.
15. Try connecting to the Internet now. You should have dial tone and
be able to hear your modem dialing.

Q: I can hear my modem dial the number, but I still get an error message.
- This could be a number of things. There are many different errors
that can happen even though you hear the modem dial. The Technical Support team
needs to know exactly, word for word, what the error is on your screen in order to
troubleshoot the connection correctly. Many of the errors are similar in description but vary slightly.
If possible, leave the error message on the screen when you call technical support.

Q: "Remote Server Is Busy or Computer Is Not Answering..."
- Try dialing the telephone number with your normal phone. If you get a busy signal,
then it is truly busy. If that is not the case, chances are you are dialing the wrong dial up access number. Make sure you
are dialing the correct number for your county. Look in the "Connect To" window to see the number you're modem is dialing.

Q: "I can connect, but get disconnected or the modem just stops."
- A good quality modem makes a big difference in the quality of
your connection. Cheaper modems are not as good at dealing with
line noise while making connections, and are missing features
that improve speed and take advantage of error correction. Not all modems
are created equal. There are good quality modems and bad quality
modems. This is similar to a good quality "Walkman" and a bad quality
"Walkman". Basically you get what you pay for. We've found that some
of the cheaper brands have trouble connecting, have small compression
dictionaries, have trouble holding a connection, and tend to "crash", "fall asleep",
"disconnect" or "drop connection" often. We have also found that
if you go with a major manufacturer, you get better technical support
if a problem develops.
- Another reason for disconnects is due to a feature (or bug) with several high speed modems.
The modems have the capability to 'adapt' to line conditions and shift to the appropriate
speeds. However, sometimes when these shifts occur, the modems have a
tendency to drop the connection. Most of these problems can be fixed by
contacting the modem manufacturer for an EPROM/software upgrade.

Question: My Modem Won't Reach The Highest Speed!
- Check the setting for maximum speed in the Dial-Up Network
settings. To check the Maximum Speed setting in Dial-Up Networking,
double-click on the My Computer | Dial-Up Networking, highlight your
Internet Junction icon, go to File, then click on Properties.
While in Properties, click on the Configure button. You should be
able to change your maximum speed here. DO NOT check the box
"Connect At This Speed Only".
- You may have a USR modem.
Internet Junction uses ASCEND hardware, which uses Rockwell tecnology.
Consequently, you may not connect at the highest possible speed due to
hardware incompatibility. Recommendation: Use the Windows standard 28,800
driver or obtain a Rockwell based modem. You may also want to try using an
initialization string to correct this.
We have a number of them available for you to try here.
You can find more init. strings at the bottom of that page.

Q: What's An Initialization or Init. String?
Some particular modems experience problems getting or staying connected.
Often these problems can be reduced or eliminated by using the proper
modem initialization string. An initialization string forces the modem to use the command
that you give it, overriding its internal dialing instructions.
It seems that almost every modem brand and
model has its own variation of the "Hayes AT Command Set" and
"s-register" settings -- there are literally hundreds of variations.
Detailed discussion of modem initialization strings is beyond the scope
of this page, but in general it is recommended that you read your modem documentation carefully,
and don't put more into the string than is necessary. As an example,
with a Supra on a PC, the string AT&F2 is an adequate initialization
string for many users; for a USR modem, AT&F1 is frequently adequate.
These two examples demonstrate using a "template" -- a pre-defined
set of modem initialization codes which can be invoked with a single
command. Most modems contain one or more default templates for
different common situations, and also let you save your own custom
"default" string. Many users use an init string that calls up a
template, and then invokes a few custom commands to tailor the
defaults.
The path to change or input an initialization string in Windows 95/98 is as follows...
My Computer | Dial Up Networking | Internet Junction Properties | Configure | Connection | Advanced | Extra Settings
We have a number of them available for you to try here.
Read your modem docs to see if one of your modem
manufacturer's default templates will work for you
(at least as a starting point). You can also
Ask Mr. Modem
what initialization string he recommends.

Q: What is K56flex technology?
The 56K technology is the elimination of the analog loop at
the Internet Service Provider(ISP). Since most ISP's access lines
are digitally terminated, transmissions don't have to be converted
back to analog. This eliminates one analog loop, lowers noise
levels, and allows the higher data transmission rates.
K56flex means substantially higher throughput in downloading Web
pages, as well as improved performance of audio/video applications
over the Internet. K56flex technology offering up to 56K speeds
over ordinary telephone lines. (provided you meet the required
parameters) By allowing downstream speeds up to 56K from the ISP
to user, K56flex significantly speeds up the delivery of information.
Graphics, interactive Web sites, audio/video, and software files will
download at near 56K ISDN speeds and at twice the rate of the prevailing
28.8K standard.

Q: What is X2 (56Kbps) Standard?
X2 technology allows modems to receive data at up to 56Kbps over
the standard, public switched telephone network(PSTN). X2 overcomes
the theoretical limitations imposed on the standard.
Typically, the only analog portion of the phone network is the
phone line that connects your home to the telephone company's
central office. Over the past two decades, the telephone companies
have been replacing portions of their original analog networks with
digital circuits. But the slowest portion of the network to change
has been the connection from your home to the central office. That
connection will likely be analog for some years to come.
X2 products are capable of 56Kbps downloads; however, due to FCC
rules which restrict power output of your service provider's modems,
current download speeds are limited to 53Kbps. Actual speeds may
vary depending on line conditions. An X2-capable analog phone line
and X2 capable service provider are necessary for these high-speed
downloads.
X2 technology is asymmetric. It sends and receives at different
speeds to take advantage of the digital connections most ISPs have
to the public phone network.

Q: What is Required for 56K and How Does it Really work?
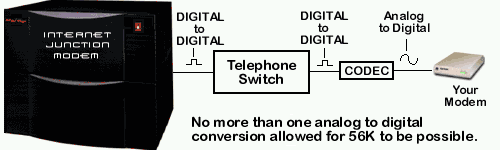
In summary the following criteria must be met for 56K to work:
- The ISP must provide 56K capable server.
- The user must use a 56K capable and compatible modem (56 KFLEX or V.90).
- The phone company must provide a phone line route to the ISP with only ONE Analog to Digital conversion.
A more Technical explanation of 56K is as follows:
56K technology takes advantage of the "mostly upgraded" digital phone
line network. The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), which is
maintained by telephone companies, has been upgrading to digital lines
between the various Central Offices (CO) over the past few years. (A PSTN
is the entire phone network and a CO is a type of switching station that
routes a call to a destination point or passes it on to another CO).
Before digital the standard in voice communication was Analog which
transmits data in the form of Waves vs. the 1's and 0's used in digital
transmissions. The phone lines between your home (or calling location)
and your closest CO is still Analog and will be for many years to come
(unless you purchase an ISDN line). Analog is sufficient for voice
communications but imposes limits on data transmission.
A data conversion between Analog and Digital limits the communication
channel to 33.6K which is the theoretical V.34 limit. This is why sending
is limited to 33.6K in 56K (your home phone line is Analog and it is
converted to digital when it hits the CO). A data conversion between
Digital and Analog does NOT limit the communication channel, and this is
the key to 56K. The 56K server passes the data to the CO in a digital
form. Assuming the data arrives to your local CO without converting
between Analog and Digital again you will be able to receive data at
speeds up to 53.3K! If the modem detects more than one Analog to
Digital conversion in the PSTN it will automatically adjust to a V.34
connection (33.6K or lower). Additionally, many phone lines, particularly in
high-population growth areas, are multiplexed together(meaning they share
one connection) using a device called a subscriber line concentrator, or SLC.
If the SLC is able to connect digitally to the phone company's central office,
it makes only one conversion. Many older central offices, however, can connect
to an SLC line only if the signal is converted to analog form first.
Then the central office reconverts the analog phone signal to digital network.
The result of two conversions a signal that's too noisy and distorted to work at 56K.
Similarly, 56K will not work through the conversion commonly done in a hotel or business
telephone system. So in most cases you can give up the dream of achieving
fast connections from the office phone or when you are traveling. Another scenario
is being goegraphically located more than 3 miles from the switching station in your neighbrhood.
If you are more than 3 miles from this switch, higher speeds are not possible -
as more than one analog-to-digital conversion has taken place.
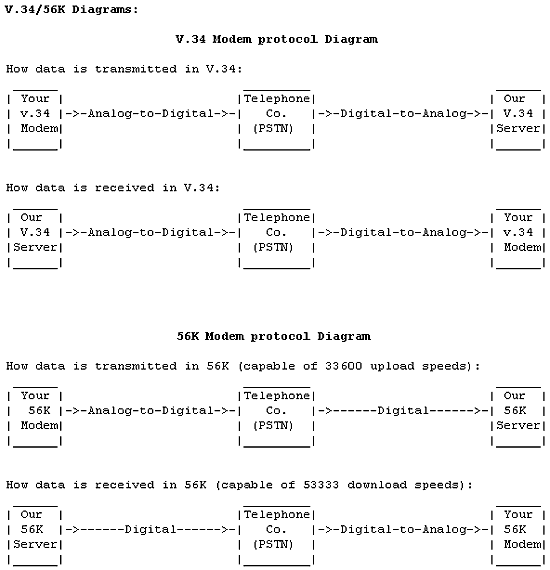
Q: Why doesn't 56K work for me (I connect 33.6 or lower)?
If you are getting a connection rate of 33.6K or lower then you are
getting a V.34 connection vs. a 56K connection (one exception is 33,333
which is the lowest 56K connection). If this is the case one of the three
required components of a 56K connection is lacking. See the summary
above for a list of the required components of an 56K connection.
We provide V.90 capable servers on all access numbers so the problem is within
the Phone Company Network (PSTN) meaning there is more than ONE
Analog-to-Digital conversion (this assumes you are using a V.90 or 56KFLEX
capable modem). Your phone company provides a voice network
and is not mandated to provide a call routing scheme with only
one Analog to Digital conversion. Only ISDN offers a digital connection.

Q: Why am I not connecting at 53K (i.e. 45K)?
Phone lines limit V.34 and 56K connections. These connection speeds
are decreased by line noise in Analog phone signals. Since there is an
analog portion in an 56K connection (between your home and the CO) this
will limit the connection rate. The length and quality of the phone
lines between your home and the first CO are the determining factor of
your connection speed. Normal 56K connection speeds will be in the range
of 42K to 47K. The highest connection speed, because of the FCC
regulations should be 53K.

Q: Why did 56K work for me at one time or work from other locations?
56K may work for you then suddenly stop or never work then suddenly
start working at any time. Also you may plug you modem into to another
location around the corner and obtain 56K connections or dial another
access number or provider and obtain 56K. This is all normal because the
availability of 56K depends on your call routing which may change at
anytime. You also may notice you can obtain 56K connections only at
certain times. This is because your phone company may have different
routing schemes based on the time of day. Again there is nothing an ISP
can do regarding these issues.

Q: Is there any Troubleshooting for 56K?
Unfortunately the available troubleshooting for 56K is limited and does
not always give accurate results. The only sure way to troubleshoot
a 56K connection is by having your phone lines traced. Please remember
a straight digital pathway is not mandated because a phone company
provides a voice communication system. If you require 56K be advised
ISDN is the ONLY guaranteed digital connection.
To troubleshoot the lack of an 56K connection using a V.90 or x2 modem
do the following (see the Next set of steps for performance problems):
- We upgrade our V.90 firmware from time to time.
You may want to obtain and apply the latest firmware for your modem
model. The V.90 standard is advertised as resolving some of the incompatibilities
x2 had with the phone network (this will not resolve the issue of
multiple analog to digital conversions). Contact your modem
manufacturer for further information. A list of modem manufacturers can be found here.
- Finding out, from your phone company, how many analog-to-digital
conversions there are between your home and our V.90 server (there
should only be one). The only way to do this is have the phone company
go on site and trace. Remember, your phone company provides a voice
network and this is not a requirement. ISDN is the only guaranteed
method for 56K and higher connections. Other items that can cause
problems in the PSTN include:
- The total number of CO's that your connection passes through (the
higher the number the more possibility of an Analog to Digital
conversion along the path).
- Copper and Microwave based network paths (fiberoptic networks will
give the best results).
- Certain switches and pads used at the various Central Offices.
- A V.90 Line Test provided by a major modem manufacturer does not prove much. It can only prove
the path between the manufacturer BBS and your home has only one Analog to
Digital conversion. You may pass this test and not be able to use
V.90 and vice versa. Usually this test will pass because you are
accessing the main PSTN backbone via a long distance carrier which is
fully digital.
- If you want us to research a problem with your 56K connection we need
the following information before we can assist. You need to call the
phone company and find the following:
- The Name of each CO you pass through along the path between your
home and our equipment (this helps in identification).
- The Switch and Pad types used by each CO.
- The signal strength of your phone signal at each CO.
- You should also use "Enhanced Phone Line Services" (this is a
service available from most phone companies for data services).
- Submit this information via the on-line technical support form. Please put this information in the comments field.

To troubleshoot performance problems with 56K do the following:
Many performance problems are seen with 56K including disconnections and
constant poor throughput. It may be best to obtain the Modem Help
guide if you have problems after following the procedures listed here.
-
Lower your port speed to 57600 or 38,400 (in Windows 95/98/NT go to My Computer,
Dial-Up Networking, highlight the Internet Junction Icon and choose
File then Properties from the menu bar. Click the button Configure
and set the maximum speed to 57600 or 38,400. Click the Connection tab then
the Port Settings button. Lower both Buffer settings to the lowest
notch and uncheck Use FIFO buffers). Retry the connection and if it
solves the problem slowly increase these settings. If using an
external modem verify your UART chip is 16550 or 16650 under Modem Diagnostics.
- Contact your modem manufacturer for the latest Modem drivers and/or firmware revision (this may include updating your modem to V.90).
- Other issues may be resolved by adding various modem commands to the
Modem Initialization string. In Windows 3.x, OS/2 and Macintosh
machines go to your Internet dialer modem settings. There should
be an option to create a new modem. Simply append a command to the
end of the existing modem string. In Windows 95/98/NT go to the
Modems icon in Control Panel. Highlight your modem, click Properties,
click the Connection tab and then the Advanced button. Type the
commands in the Extra settings field (do not add an AT).
Note: These modem commands may not be universal for all modem models and
firmware revisions. It is always best to check your modem manual
or contact the modem manufacturer directly, for these settings.
Try each one of these commands one at a time and test your
connection, in other words use "trial and error." You can combine
commands, i.e. disable V.42 and Compression would be &K0S15=128.
- USR (all models) Disable Compression - &K0
- USR Sportster Model Modems
- Disable V.42 Error Control (forces MNP5) - S15=128
- Disable x2 - S32=34
- Disable V.90 - S32=66
- Disable both x2 and V.90 - S32=98
- USR Courier Model Modems
- Disable V.42 Error Control (forces MNP5) - S27=32
- Disable x2 in a USR Courier - S58=1
- Disable V.90 in a USR Courier - S58=32
- Disable both x2 and V.90 in a USR Courier - S58=33
- Disable Flex in Zoom modems - S58=0
- Disable V.90 in Zoom modems - S95=1+MS=11
- Disable Flex (Motorola - Hayes) to 33,600 or less - +MS=11,1,300,33600
- Disable Flex (Motorola - Hayes) to 14,400 or less - +MS=10,1,300,14400
- Disable Flex (Motorola - Hayes) to 9,600 or less - +MS=9,1,300,9600

Q: What's wrong? The first call I place to my ISP isn't at 53 or even 40Kbps but a measly 28.8-Kbps
or slower connection.
Signals from 56K modems are delicate. They tolerate only one analog-to-digital
conversion along your phone line. In most cases, the signal from the line
is converted from analog to digital only once, at the phone company's central
office. From there it travels to your ISP, which has a digital connection.
But many phone lines, particularly in high-population growth areas,
are multiplexed together(meaning they share one connection) using a device
called a subscriber line concentrator, or SLC. If the SLC is able to connect
digitally to the phone company's central office, it makes only one conversion.
Many older central offices, however, can connect to an SLC line only if
the signal is converted to analog form first. Then the central office reconverts
the analog phone signal to digital network. The result of two conversions
a signal that's too noisy and distorted to work at 56K. Similarly, 56K
will not work through the conversion commonly done in a hotel or business
telephone system. So in most cases you can give up the dream of achieving
fast connections from the office phone or when you are traveling. Another scenario
is being goegraphically located more than 3 miles from the switching station in your neighbrhood.
If you are more than 3 miles from this switch, higher speeds are not possible -
as more than one analog-to-digital conversion has taken place.

Q: Before I call the technician, what do I have to prepare?
- Have the computer on and your Windows 95/98 cd-rom handy
- The error you're getting on the screen
- Your User Name and Password
- Know the number from which your modem dials
- What operation system you are using (Win 98, Win 95, Win 3.x, Mac)?
- Make and model of your modem
- What kind of chipset (TI or Rockwell or...)?
- What software you are using to run AT commands (Quicklink or Bitware or Super Voice)
- Which com port your modem is using.
|